VTEnc v0.3.0
Today I’m releasing VTEnc v0.3.0. It features a complete re-design of the library API, a bugfix, decoding performance improvements and other changes aiming to improve code maintainability.
New API
Version v0.3.0 brings in a fresh and completely re-thought API. That means that none of the functions/structures from previous versions will look the same or even exist.
It introduces the new encoding/decoding handler type vtenc. This opaque structure will hold the context to encode and decode sequences, while hiding the details to the user. It’s a replacement for the VtencEncoder and VtencDecoder types, which were used on previous versions. The initialisers for those old types (vtenc_encoder_init() & vtenc_decoder_init()) has also been removed in this version.
vtenc handlers must be created with vtenc_create() and destroyed after being used with vtenc_destroy(). So, code using the VTEnc library will probably look somewhat like this:
vtenc *handler = vtenc_create();
/* use `handler` to encode and/or decode */
vtenc_destroy(handler);
Another important change in this release is the addition of vtenc_config(). This function lets you set configuration options that will determine how the encoding and decoding functions perform. At the moment, you can only set the encoding parameters, but this new approach opens the possibility of configuring handlers in different ways in the future. Here’s an example of using the function:
vtenc_config(handler, VTENC_CONFIG_ALLOW_REPEATED_VALUES, 0);
vtenc_config(handler, VTENC_CONFIG_SKIP_FULL_SUBTREES, 1);
vtenc_config(handler, VTENC_CONFIG_MIN_CLUSTER_LENGTH, 32);
Finally, the encoding and decoding functions’ signatures have been modified too. These functions now take a vtenc handler as their first argument and return an integer indicating its result code.
Decoding performance boost
The decoding algorithm has been refactored to reconstruct the output sequence in a more efficient way. It avoids unnecessary switch contexts by “memoising” higher bits on each visited node when traversing the Bit Cluster Tree. You can read about the details of this technique on PR #29.
The results of this work are amazing:
- An increase of decoding speed in the range of 20-55% for
gov2.sorteddata set. - An outstanding increase of decoding speed of 1,000% (10x faster) for
ts.txtdata set.
| gov2.sorted | ts.txt |
|---|---|
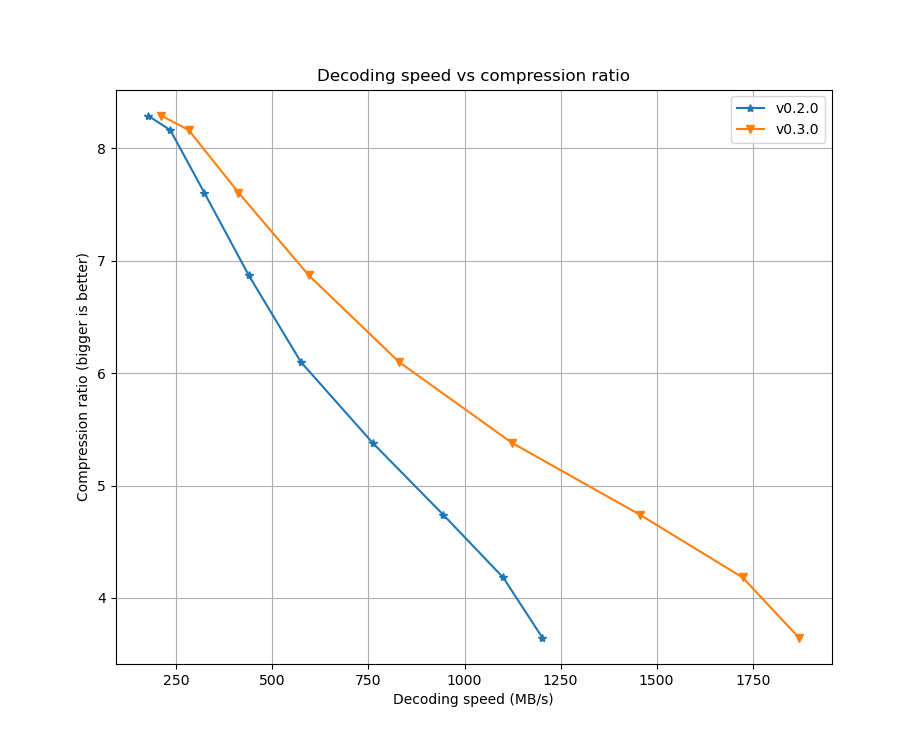 |
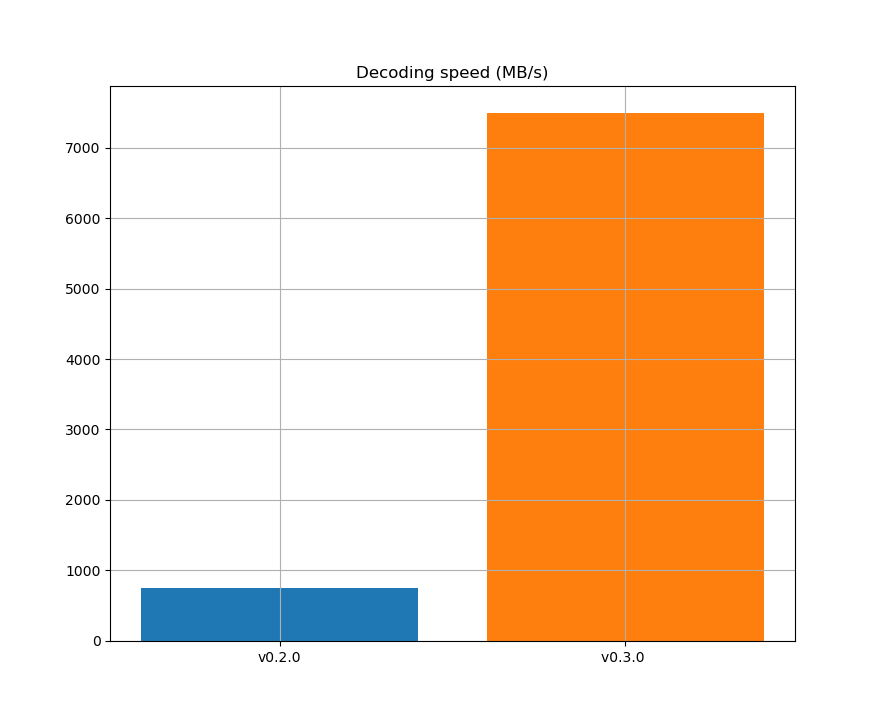 |
Coding style
This release establishes a coding style guide for the project. The new “CODING_STYLE.md” document lists a set of rules that must be followed when adding or updating code. It’s by no means exhaustive nor complete, but it’s nonetheless a starting point.
The coding style guide is an attempt to bring in consistency, which I believe is an important part of keeping your code readable. It also removes some of the burden of making decisions, specially those with regards to coding aesthetics.